One common example of a price ceiling is rent control. It is determined by interaction of supply and demand.

Equilibrium Price Formula Calculations How To Find Equilibrium Price Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
It is set by the government 21 When quantity supplied equals quantity demanded what.
. See the answer See the answer done loading. The quantity supplied and the quantity demanded are equal. If there is a ceiling price below the equilibrium level a decrease in demand will worsen the shortage.
Decrease in supply on the other hand results in an increase in price. If the equilibrium price is 6 and the government says you cannot charge more than 8 the government intervention is meaningless or non-binding. When a market is not in equilibrium A.
If both the changes are proportionately equal equilibrium price will not change. While adding up the surplus of every party is simple with just consumers and producers it gets more complicated as more players enter the market. Firms will increase contributions to political action committees.
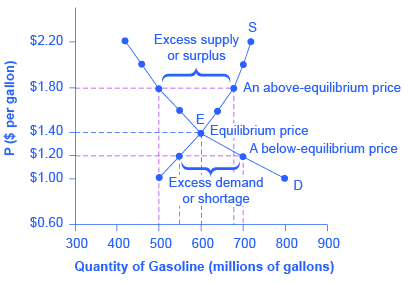
The market does not clear-This is incorrect since the market clears when demand equals supply and there is no shortage or surplus. Specifically for any price that is lower than 60 the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded thereby creating a surplus. Market Surplus 450 450 900.
Choose all that apply. Decrease in demand results in a fall in equilibrium price. To find the equilibrium price set the demand and supply equations equal to each other.
Which of the following is true of market social equilibrium if third parties people outside the market for a good bear part of the cost of the goods production. Therefore the price of 60 is the equilibrium price. Whereas price ceiling aims to lower the price price floors aim to raise it.
An increase in demand and a. Question 4 Which of the following is true regarding the equilibrium price in perfectly competitive markets in the long run. P 80 - Q P 80 - 18 P 62.
It is set by the government. Which of the following statements is TRUE at a markets equilibrium price and quantity. At the new equilibrium the equilibrium price falls from 325 to 250 but the equilibrium quantity increases from 250000 to 550000 salmon.
It will equal the firms long- and short-run average costs but not its marginal cost. Identify the new equilibrium and then compare the original equilibrium price and quantity to the new equilibrium price and quantity. We need to make the quantity supplied equal to the quantity demanded in order to determine the equilibrium price.
Which among the following statement is not true. It is always a fair and just price. This means that the amount of product the consumers want to buy Demanded Quantity is equal to the amount of that product the producers want to sell Supplied Quantity.
Qs Qd 128 8P 478 - 6P 128 8P 6P 478 8P 6P 478 -128 14P 478 -128 14P. Government intervention is required to achieve equilibrium. At any other price level there is either surplus or shortage.
The equilibrium price is 10 and the equilibrium quantity is 10. There is a pressure for the price to increase. An increase in supply means that the supply of a good increase at each level of price.
The gains from trade are minimized. It will equal the firms long-run average costs and. Producer surplus is the area above the supply curve but below.
In Figure 36i a different process is outlined. Goods are purchased by buyers who value them the most. It is also in as the market clearing price.
Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied are the same. Yes the equilibrium price is the only price in the market where both the plans of the producers and the plans of the consumers agree on. At the competitive equilibrium price which of the following is true.
Indicate whether the statement is true or false. Correct option is B An increase in supply would cause a decrease in market equilibrium price and an increase in equilibrium quantity. Which if the following statements about equilibrium price are true.
Producer surplus yellow 300 x 32 450. To find our equilibrium tax inclusive price we substitute our equilibrium quantity into one of our equations. Use the basic rules of algebraic equations to solve for P or the price.
Shortage occurs when the quantity demanded is beyond what the current supply is at a. 100 1P 400 5P subtract 1P from both sides of the equation 100 400 4P subtract 400 on both sides of the equation -300 4P divide by 4 on both sides of the equation -75 P. As the price falls to the new equilibrium level the quantity supplied decreases to 20 million pounds of coffee per month.
This mutually desired amount is called the equilibrium quantity. Ill substitute it into our demand equation. 80 - Q 26 2Q 54 3Q Q 18 Thus our equilibrium quantity is 18.
A Decrease in Demand. Quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded. A price ceiling set above the equilibrium price causes a surplus in the market.
All consumers can buy all they demand. A Demand b Supply c Both a and b d None of the above. Panel b of Figure 310 Changes in Demand and Supply shows that a decrease in demand shifts the demand curve to the left.
When a market is at equilibrium pricing demand equals supply and equilibrium quantity and price are both reached. A Demand of labor is done by the producer b Demand of labor depends open its productivity c Marginal. The area of the triangle representing consumer surplus is CS 20-1-10250.
Which factors help in the determination of equilibrium price. It will equal the firms long- and short-run average costs and also its marginal cost. Firms are price gouging.
The economic motives of sellers and buyers will. Economics questions and answers. Since this seems backwards it is easy to get confused about when price ceilings and price floors are binding.
The equilibrium price falls to 5 per pound. D None of the above. Consumer surplus plus producer surplus is maximized.
Consumer surplus is measured by the area of the triangle below the demand curve but above the equilibrium price for the quantities between zero and the equilibrium quantity. Such an increase in supply creates a surplus in the market which drives the price downward. Which of the following is not true of equilibrium price.
The lowest-cost producers manufacture the goods. Socially optimal quantity will be greater than the private quantity and the socially optimal price will be greater than the private price. The equilibrium price is the only price where the desires of consumers and the desires of producers agreethat is where the amount of the product that consumers want to buy quantity demanded is equal to the amount producers want to sell quantity supplied.
Solve for the equilibrium price.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/EquilibriumQuantity-3d51042295814ceda425f70c182d9e76.png)
Equilibrium Quantity Definition

Market Equilibrium Article Khan Academy

3 6 Equilibrium And Market Surplus Principles Of Microeconomics

3 6 Equilibrium And Market Surplus Principles Of Microeconomics
0 Comments